The WordPress Database Management Guide (Beginner Friendly)
The WordPress database is a critical component that underpins the functionality of your website, storing essential data such as posts, comments, and user information. Becoming acquainted with the WordPress database structure is a vital consideration for any site admin looking to optimize their day-to-day and avoid any unpleasant surprises to performance.
The WordPress database is a critical component that underpins the functionality of your website, storing essential data such as posts, comments, and user information. Becoming acquainted with the WordPress database structure is a vital consideration for any site admin looking to optimize their day-to-day and avoid any unpleasant surprises to performance.
This guide explores the fundamentals of the database. You’ll learn how to access your database using tools like phpMyAdmin, perform essential operations such as creating and backing up databases, and implement maintenance practices to keep your database optimized.
Additionally, we address common database issues and security best practices to safeguard your data, with advanced management techniques for handling complex scenarios with confidence. Read on, and you’ll discover everything worth knowing about WordPress database management.
Key Points
- How to implement security best practices help to protect the database from unauthorized access and vulnerabilities.
- The WordPress database is essential for storing and managing all site data, including posts, comments, and settings, using MySQL as its management system.
- Understanding the database structure, which includes core tables like wp_posts, wp_users, and wp_comments, is crucial for efficient data retrieval and manipulation.
- How to access the database using phpMyAdmin, where users can perform operations such as creating databases, backups, and optimizations.
- Why regular maintenance tasks, including backups and optimizations, are vital for ensuring the integrity and performance of the database.

Part 1: Database Fundamentals
The database serves as the backbone of your site, storing all content, settings, and user information. By familiarizing yourself with how the database operates and its structure, you’ll be better equipped to troubleshoot issues, optimize performance, and ensure data integrity.
What is a WordPress Database?
A WordPress database is a structured collection of data that stores all the information required for your website to function properly. To manage this data, it primarily uses MySQL, a popular relational database management system. However, WordPress is also fully compatible with MariaDB, a high-performance fork of MySQL that many hosting providers now prefer for its enhanced speed and scalability. Both systems work smoothly with WordPress, empowering your site to handle data efficiently and perform at its best.
As you can see, the database plays a crucial role in the operation of your site by allowing dynamic content generation and efficient data retrieval. The basic definition of a WordPress database encompasses various types of information, including posts, pages, comments, user profiles, and site settings. Each piece of content is stored in specific WordPress database tables, organized in a way that allows for quick access and manipulation.
WordPress relies on MySQL or MariaDB to handle these operations through SQL (Structured Query Language) commands. This interaction enables users to perform tasks such as creating new posts or retrieving existing content.
Databases are essential for WordPress because they provide a centralized location for storing all site-related data. Without a database, WordPress would not be able to load content or maintain user interactions effectively. Understanding how this system works empowers users to manage their sites more efficiently and troubleshoot issues when they arise.
Get SolidWP tips direct in your inbox
Get started with confidence — risk free, guaranteed
Database Structure and Components
WordPress database structure (or DB structure) consists of several key components organized into tables that store different types of data. The primary database used by WordPress is MySQL, which organizes data into tables that can be easily accessed and manipulated.
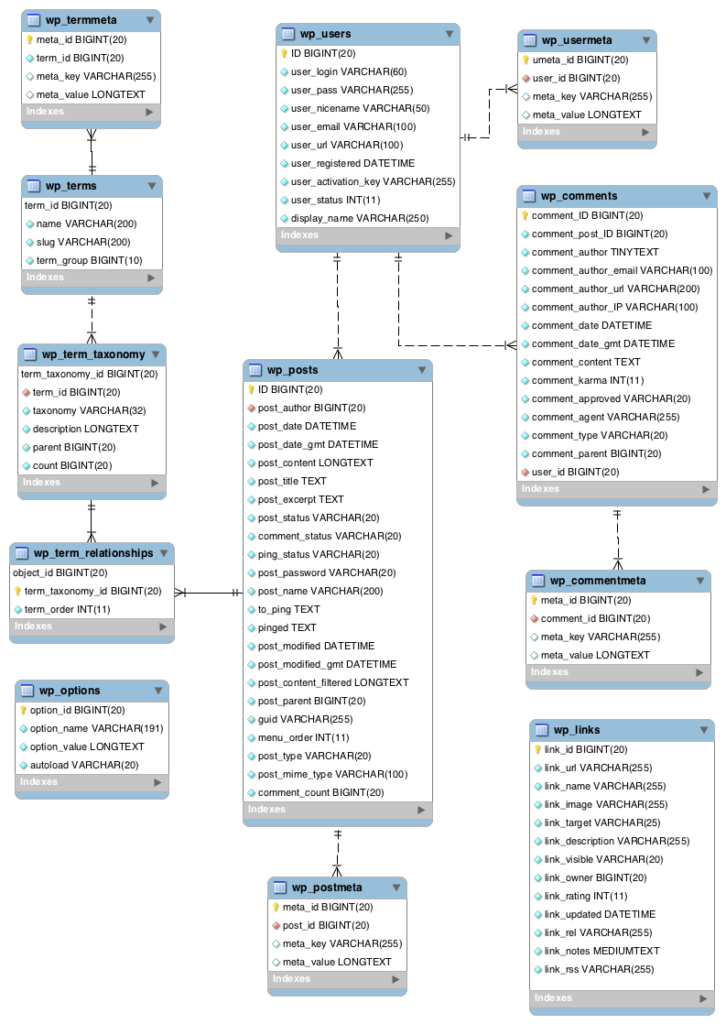
In a typical installation, there are several core WordPress database tables that each serve distinct purposes:
- wp_posts: This table contains all types of content, including posts, pages, attachments, and custom post types.
- wp_users: It stores user information such as usernames, passwords (hashed), email addresses, and roles.
- wp_comments: This table holds comments made by users on posts or pages.
- Wp_options: It contains various settings and configurations for your site, such as site URL and active plugins.
Each core table has specific fields that define its structure. For instance:
- The wp_posts table includes fields like ID, post_title, post_content, post_status, and others that describe the post’s attributes.
- The wp_users table contains fields such as user_login, user_email, user_registered, etc., which help manage user accounts.
Data within these tables is organized into rows and columns. Each row represents a unique entry (e.g., a single post or user), while columns represent the attributes associated with that entry (e.g., title or content). Such a WordPress DB structure allows for efficient querying and retrieval of information.
WordPress utilizes relationships between tables to connect different types of data. For example:
- The wp_comments table links back to the wp_posts table through the comment_post_ID field. This relationship allows comments to be associated with specific posts.
- Similarly, user roles defined in the wp_users table can determine permissions for accessing or editing content across the site.
Additionally, each table will contain a variety of fields and columns that store even more specified bits of data. For example, the wp_comments table has all of the data related to user comments on your posts and pages.
| Table Name | Description |
|---|---|
| wp_users | The list of users on your WordPress website. Users of all WordPress user roles are stored here (administrator, editor, author, contributor, subscriber, etc.) Additional user information stored in this table includes username, first name, last name, nickname, password, email, registration date, status and role. |
| wp_usermeta | Each user features information called the meta data. Metadata stored here includes a unique user ID, meta key, meta value, and meta ID. These are all unique identifiers for users on your site. |
| wp_term_taxonomy | WordPress uses three types of taxonomies, including category, link, or tag. This table stores the taxonomy associations for the terms. |
| wp_term_relationships | This table stores the relationships between posts, categories and tags. The association of links to their respective categories are also kept in this table. |
| wp_termmeta | Each term features information called the meta data and it is stored in wp_termmeta. |
| wp_terms | The categories for both posts and links and the tags for posts are found within the wp_terms table. |
| wp_posts | The core of the WordPress data is the posts. This table stores the content of any post or page that you’ve published, including autosave revisions and post option settings. Additionally, pages and navigation menu items are stored in this table. |
| wp_postmeta | Each post features information called the meta data and it is stored in the wp_postmeta. Some plugins may add their own information to this table. |
| wp_options | All settings set from the WordPress admin dashboard’s Settings page are stored here. This includes all theme and plugin options. |
| wp_links | The wp_links holds information related to the links entered into the Links feature of WordPress. (This feature has now been deprecated, but can be re-enabled with the Links Manager plugin.) |
| wp_comments | All comments published to your site are stored here, along with additional information about the comment author (name, URL, IP address, email address, etc.) |
| wp_commentmeta | Each comment features information called the meta data and it is stored in the wp_commentmeta, including comment ID number. |
Part 2: Managing Your Database
This section will guide you through accessing your database, performing essential operations, and implementing best practices for backup, recovery, and optimization. Whether you are a beginner or looking to refine your skills, this guide will provide actionable insights to help you manage your WordPress database with confidence.
Accessing Your Database
Accessing your database is a fundamental skill for managing your WordPress site. The most common tool for this purpose is phpMyAdmin, a user-friendly interface that allows you to interact with your MySQL database without needing to write complex SQL commands.
To access phpMyAdmin, log into your web hosting control panel (like cPanel) and locate the phpMyAdmin icon. Once opened, you’ll see a list of databases on the left sidebar. Selecting your WordPress database will display its tables in the main area.
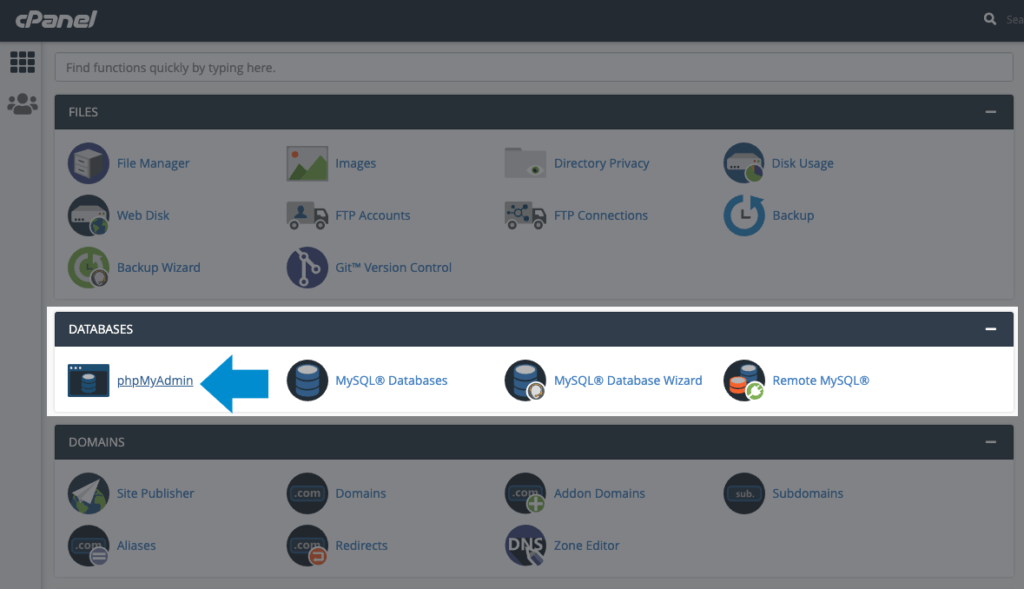
When you open phpMyAdmin, you’ll see a login screen. Here is where you’ll enter your database username and password. Once you’re in the phpMyAdmin manager, you can access databases through the tab at the top of the screen.
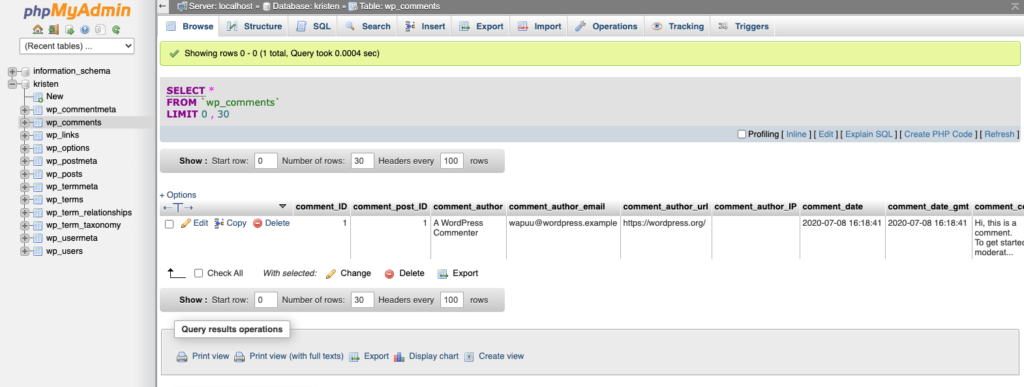
Familiarize yourself with the phpMyAdmin interface. The main sections include:
- Databases: View all databases associated with your account.
- Tables: Display all tables within the selected database.
- SQL tab: Execute custom SQL queries directly.
MySQL queries are commands used to interact with the database. Basic commands include SELECT (to retrieve data), INSERT (to add data), UPDATE (to modify existing data), and DELETE (to remove data). Learning these commands will allow you to manage your data effectively.
Remember — when accessing your database, security is paramount. Always use strong passwords for your hosting account. If possible, restrict access to specific IP addresses through your hosting provider’s settings to improve security further.
Essential Database Operations
Here, we’ll explore essential operations that every WordPress user should know when managing their database. These operations include creating a new database, backing up and recovering data, and performing regular maintenance tasks. Mastering these skills will help ensure that your website remains functional and secure.
Creating a Database
Creating a new database is a crucial step in setting up or managing a WordPress site. There are several methods for creating a database, each suitable for different scenarios.
- Automated installation method
Most web hosting providers offer automated installation tools like Softaculous that create a new database during the WordPress installation process. Simply follow the prompts during installation, and the system will handle everything for you.
- Manual creation through phpMyAdmin
If you need to create a database manually, phpMyAdmin makes it straightforward:
- Log into phpMyAdmin.
- Select the Databases tab at the top.
- Enter a name for your new database in the Create database field.
- Choose the collation (usually utf8_general_ci is recommended).
- Select Create.
Your new database will now appear in the left sidebar.
- Command line creation
For advanced users with SSH access, creating a database via command line can be efficient:
- Connect to your server via SSH.
- Log into MySQL using the following snippet:
| mysql -u username -p |
- Enter your password when prompted.
- Create a new database with this snippet:
| CREATE DATABASE dbname; |
Replace dbname with your desired name.
After creating a new database, it’s crucial to set appropriate permissions:
- Create a new MySQL user or use an existing one.
- Grant this user access to the newly created database using:
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON dbname.* TO ‘username’@’localhost’; |
If you only want to grant specific permissions (e.g., SELECT, INSERT), specify them instead of ALL PRIVILEGES:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON new_database_name.* TO ‘new_username’@’localhost’;
- Flush privileges to apply changes:
| FLUSH PRIVILEGES; |
This ensures that only authorized users can access and modify the database.
Backup and Recovery
Establishing a regular backup schedule is essential for maintaining data integrity. Consider these strategies:
- Frequency: Depending on how often you update content, schedule your backups to meet your needs.
- Storage locations: Store backups in multiple locations (local storage, cloud services) to prevent loss.
You can manually back up your WordPress database using phpMyAdmin:
- Log into phpMyAdmin.
- Select your WordPress database from the left sidebar.
- Select the Export tab at the top.
- Choose Quick export method for simplicity or Custom for more options.
Select Go to download an SQL file of your entire database.
This file can be used later for restoration if necessary. To restore, log back into phpMyAdmin and select your database:
- Select the Import tab at the top.
- Choose the SQL file you previously exported and select Go.
For automated backups, consider using a dedicated software solution like Solid Backups — NextGen:
- Cloud-first approach ensures that backups are initiated from SolidWP servers, minimizing the impact on your hosting resources.
- Off-site backups ensure your data is safe, unlike local server storage which can be compromised through hacking or unauthorized access.
- The system performs daily incremental backups, capturing only new or changed files, which saves time and storage space.
- Alongside incremental backups of altered or new files, Solid Backups — NextGen backs up the database in full.
- Features a user-friendly interface with a timeline of site activity, allowing you to select specific restore points easily.
Restoration through Solid Backups — NextGen can be achieved through a ‘one-click restore’ function:
- View the Activity Timeline to see available backups.
- Select the desired backup date to select it as your restore point.
- Select the Restore site button to begin the restoration process.
- Confirm your choice and wait for the process to complete.
Maintenance and Optimization
Establishing a routine maintenance schedule helps identify issues before they escalate:
- Database cleanup: Regularly remove old post revisions, spam comments, and unused WordPress database tables.
- Check database integrity: Use phpMyAdmin’s Repair feature on tables that may become corrupted over time. Advanced users can use the mysqlcheck troubleshooting tool. If in doubt at any time, simply contact your hosting provider’s support team.
Note: Our own security solution Solid Security Pro can help maintain database integrity through its automated vulnerability scanner, which alerts site admins of any potential issues as they occur. Furthermore, Solid Backups — NextGen allows you to restore your database to a previous state if corruption occurs or if unwanted changes are made.
You can optimize your database to improve performance by taking the following steps:
- In phpMyAdmin, select tables and choose Optimize table from the dropdown menu after selecting With selected.
- Regularly running optimization queries can help minimize space usage within tables.
For further optimization, consider using plugins like WP-Optimize or WP-Sweep that automate cleanup tasks. These plugins allow you to schedule cleanups regularly without manual intervention.
To maintain peak performance, you can also monitor slow queries using tools like Query Monitor, which helps identify which queries may need optimization. Always ensure that caching mechanisms (like object caching) are in place to speed up data retrieval from the database.
Part 3: Troubleshooting and Advanced Topics
In this section, we’ll explore troubleshooting common database issues, implementing security best practices, and delving into advanced database management techniques. With the right knowledge and tools, you can effectively resolve problems, secure your database, and manage complex data scenarios.
Common Database Issues
Common database issues can disrupt your WordPress site’s functionality, but identifying and resolving them quickly is key.
- Identifying problems: Some typical symptoms of database issues include error messages like Error establishing a database connection or Database tables are missing. These errors often indicate database server problems and downtime, corrupted tables, incorrect database credentials, exceeding database connection limits, or file permission issues.
- Repair procedures: If you suspect corruption, you can use phpMyAdmin to repair tables. Select the affected table, navigate to the Operations tab, and select Repair table. This process can fix minor issues without affecting your data.
- Error resolution: For persistent errors, consider checking your wp-config.php file for correct database credentials. If the issue continues, enable debugging in WordPress by setting define(‘WP_DEBUG’, true); in the wp-config.php file. This will provide more detailed error messages that can help pinpoint the problem.
- When to seek professional help: If you encounter complex issues that you cannot resolve, it may be time to seek professional assistance. As we mentioned earlier, tools like Solid Security Pro can help monitor your site and alert you to potential database vulnerabilities or performance issues before they escalate.
Security Best Practices
Securing your WordPress database is critical to protecting your site from unauthorized access and data breaches. Implementing stringent security measures will help safeguard sensitive information and allow you to focus on growing your business.
- User permissions: Start by managing user permissions carefully. Limit access to your database by creating specific roles with only necessary privileges. Avoid using the default admin account for daily operations; instead, create separate accounts with limited capabilities for regular users. Our Solid Security Pro plugin makes it easy to manage user groups at a granular level for the ultimate control over site access.
- Secure configuration: Ensure that your wp-config.php file is properly configured. Change the default table prefix from wp_ to something unique to make it harder for attackers to guess table names. Additionally, set strong passwords for all database users and consider using Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) to secure WordPress admin access.
- Backup security: Regular backups are essential for recovery in case of data loss or corruption. Use Solid Backups — NextGen to automate backup processes and store backups securely on SolidWP’s encrypted servers.
- Common vulnerabilities: Be aware of common vulnerabilities such as SQL injection attacks. Keep your WordPress core, themes, and plugins updated to guard against vulnerabilities. Solid Security Pro grants extra peace of mind by integrating with the Patchstack database, which patches any vulnerabilities as soon as they’re discovered.
Advanced Database Management
Understanding advanced techniques is essential for those looking to take their database management skills further:
- Custom queries: Learning how to write custom SQL queries allows you to manipulate data directly within your database. This skill can be particularly useful for bulk updates or extracting specific information that may not be readily accessible through the WordPress admin interface.
- Database migration: When moving a site from one host to another or changing its domain name, proper migration of the database is crucial. Solid Backups — NextGen simplifies the migration process by allowing users to move their WordPress site to a new location or host without needing additional tools.
- Working with large databases: As your site grows, managing large databases can become challenging. Regularly optimize tables using phpMyAdmin or Solid Security Pro, which helps identify and remove unnecessary data, such as spam comments and post revisions. If working with multiple sites, Solid Central enables easy multisite management through a centralized dashboard.
- Development considerations: When developing custom themes or plugins that interact with the database, follow best practices such as using prepared statements to prevent SQL injection vulnerabilities. Testing changes in a staging environment before deploying them on a live site is also advisable.
Healthy Databases Make Healthy Sites
As we’ve seen, effective management of your WordPress database is crucial for ensuring your website’s performance, security, and reliability. Take the knowledge you’ve gained from this guide to optimize your database for efficiency, and protect your valuable data from unauthorized access and potential threats.
To simplify your database management experience, consider using Solid Security Pro for ongoing protection against vulnerabilities and Solid Backups — NextGen for automated backup solutions that ensure your data is always safe. Our software empowers you to manage your WordPress database with confidence, enabling you to focus on growing your online presence, safe in the knowledge that your database remains in the very best health.
Sign up now — Get SolidWP updates and valuable content straight to your inbox
Sign up
Get started with confidence — risk free, guaranteed